

Astaxanthin for Healthy Aging
Astaxanthin is arguably the most powerful antioxidant on Earth. With oxidative stress and inflammation being at the core of the aging cascade,1 balancing physiological processes at the cellular level that deliver oxidative balance and anti-inflammatory activity are the unlocks for cardiovascular, joint, vision and skin health.
Today, 52 million Americans are ages 65 years old plus. By 2060, this number will reach 95 million.2 We are all interested in healthy living, so that age does not define us but instead is just a number. Putting a priority on healthy aging requires a focus on the imbalance within the aging cascade – the domino effect that can be caused by out of control free radicals and reactive oxygen species (ROS). Chronic inflammation is associated with conditions like diabetes, cardiovascular disease, muscle loss, and even dementia,1 that tip the balance of healthy aging toward morbidity, frailty and poor quality of life.
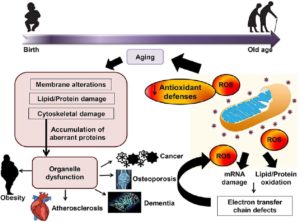
Imbalance of ROS leads to increased oxidative stress which results in damage to DNA, proteins, and lipids within the mitochondria of the cell.3 Dysfunction within the mitochondria triggers an inflammatory response by activating NF-?B signaling pathway and secretion of other inflammatory cytokines.4 But, there is a body of science that helps us understand how astaxanthin can naturally balance oxidative stressors and inflammation at the cellular level to support the aging process.5 Valensa’s solution, Zanthin® Natural Astaxanthin, is backed by science that shows an important role for this powerful antioxidant in cardiovascular issues, joint discomfort associated with pain and inflammation, and vision health, such as eye fatigue. Astaxanthin is also important in skin health and elasticity, another important factor in how we feel as we age.6,7
As discussed in our white paper, Zanthin Natural Astaxanthin has been shown to act as an immunomodulator, eliciting a proper immune response to manage inflammation and rebalance the body.8 This impressive natural antioxidant has been shown to downregulate pro-inflammatory cytokines and up-regulate anti-inflammatory cytokines, allowing the body to rebalance in response to physiological stressors and regain cellular function.9 And, pre-clinical and clinical studies have demonstrated the benefit proposition of Zanthin in a joint health solution formulation, FlexPro MD®, for faster and sustained relief from joint pain.9,10,11
Zanthin Natural Astaxanthin also has an established role in vision health,12 where oxidative stress and consumer’s dedication to smart technology take a toll on the aging eye. EyePro MD®, containing Zanthin, has been scientifically developed to address both the cellular processes that impact eye health,13 as well as lifestyle and environmental stressors that can lead to dry eye, eye fatigue, and ocular diseases.14,15
For a healthy, active lifestyle, the role of Zanthin is clear – established support to cardiovascular, joint, and vision health, coming from a powerhouse of nature, that can effectively be harnessed by Valensa to bring you benefit propositions like FlexPro MD and EyePro MD. So, make the most of your years. Unleash the power of Zanthin® Natural Astaxanthin so that age does not define you, but instead is just a number.
Valensa’s Zanthin® Natural Astaxanthin is available as a stand-alone ingredient, and is also used in Valensa’s FlexPro® MD formula.
Get a colorful Infographic that simplifies how Zanthin Natural Astaxanthin works here.
- Ferrucci and Fabbri. 2018. Nat Rev Cardiol. September;15(9):505-22.
- https://www.prb.org/aging-unitedstates-fact-sheet/
- Valko, et al. 2007. Inter J Biochem Cell Biol. 39:44-84.
- Kim and Kim. 2018. Nutrients. 10(9):1137;doi:10.3390/nu10081137.
- Kakhri, et al. 2018. Pharmacol Res. 136:1-20.
- Davinelli, et al. 2018. Nutrients. 10:522;doi:10.3390/nu10040522.
- Ito, et al. 2018. Nutrients. 10:817;doi:10.3390/nu10070817.
- Park, et al. 2010. Nutr Metab (London). 7:18.
- Park, et al. 2016. J Med Food. 19(12):1196-1203.
- Valensa clinical study final report – data on file. Available on request.
- Park, et al. 2020. Nutrients. 12:956;doi:10.3390/nu12040956.
- Piermarocchi, et al. 2012. Eur J Opthalmol. 22(2):216-25.
- Pinazo-Durán, et al. 2014. Clin Interven Aging. 9:637-52.
- Giannaccare, et al. 2020. Mar Drugs. 18:239;doi:10.3390/md18050239.
- Yang, et al. 2020. Exp Mol Pathol. 113:104372;doi:10.1016/j.yexmp.2020.104372.
